- Inicio
- Universidad
- UAL Crop Nitrogen and Irrigation Lab
UAL Crop Nitrogen and Irrigation Lab
Research
Simulation models of crop growth, N uptake and water use
Detailed knowledge
of crop N uptake and water use (ETc) are essential information for
optimal N and irrigation management of crops. In farming practice, N
uptake and ETc vary appreciably between individual crops because of
differences in planting dates, climate etc. Simulation models, with few
and readily available inputs can provide accurate estimations of daily
crop N uptake and ETc.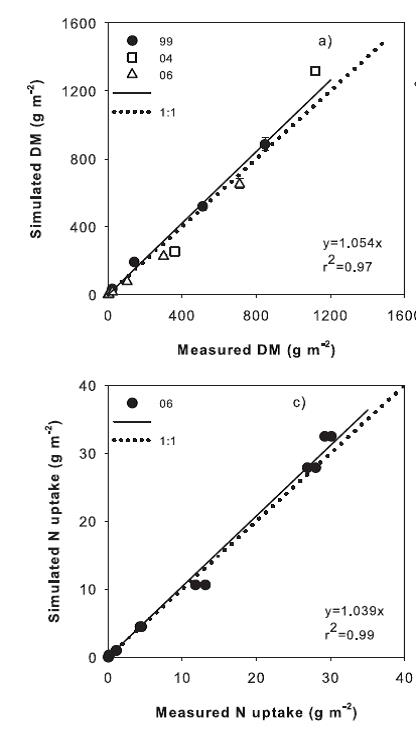
The VegSyst
simulation model calculates crop N uptake, ETc and crop growth for
green-house-grown vegetable crops. Its inputs are simple climatic data
and planting date. Long term average climatic data can be used to
develop a plan before planting. VegSyst has been calibrated and
validated for tomato, pepper and melon. It is currently being
calibrated for the rest of the major vegetable species in Almeria.
VegSyst is being adapted to open field conditions. See Gallardo et al
(2011) and Giménez et al. (2013).
EU-Rotate_N is a
well-established model developed model developed to deal with different
open field crops throughout Europe. EU-Rotate_N has been adapted to the
conditions of greenhouse production in SE Spain. It has been calibrated
and validated for tomato, pepper and melon. EU-Rotate_N simulates crop
N uptake, ETc, growth, fruit production, drainage, nitrate leaching and
mineral N in soil. It is a particularly useful model to demonstrate to
growers and policy makers how different crop management scenarios
influence production and nitrate loss the environment.
Internationally,
CropSyst is one of the most important crop simulation models. It has
been used mostly with cereal crops. Currently, in collaborative work
with Washington State University and the University of Cordoba, it is
being adapted to vegetable crops, including greenhouse grown crops.