DSL (Digital Subscriber Line)
Vicente González Ruiz
September 12, 2016
Contents
1 History
- Bellcore (now Telcordia Technologies) developed Asymmetric Digital
Subscriber Line (ADSL) and filled a patent in 1988.
- Now is the most used method for residential access.
2 Hardware
- Use the same line than the telephone (ordinary copper lines).
- A DSL modem is the device required to connect the computer or the
network of the user to the telephone line.
- The local loop (last-mile) must be less than 5.5 kilometers (3.5 miles).
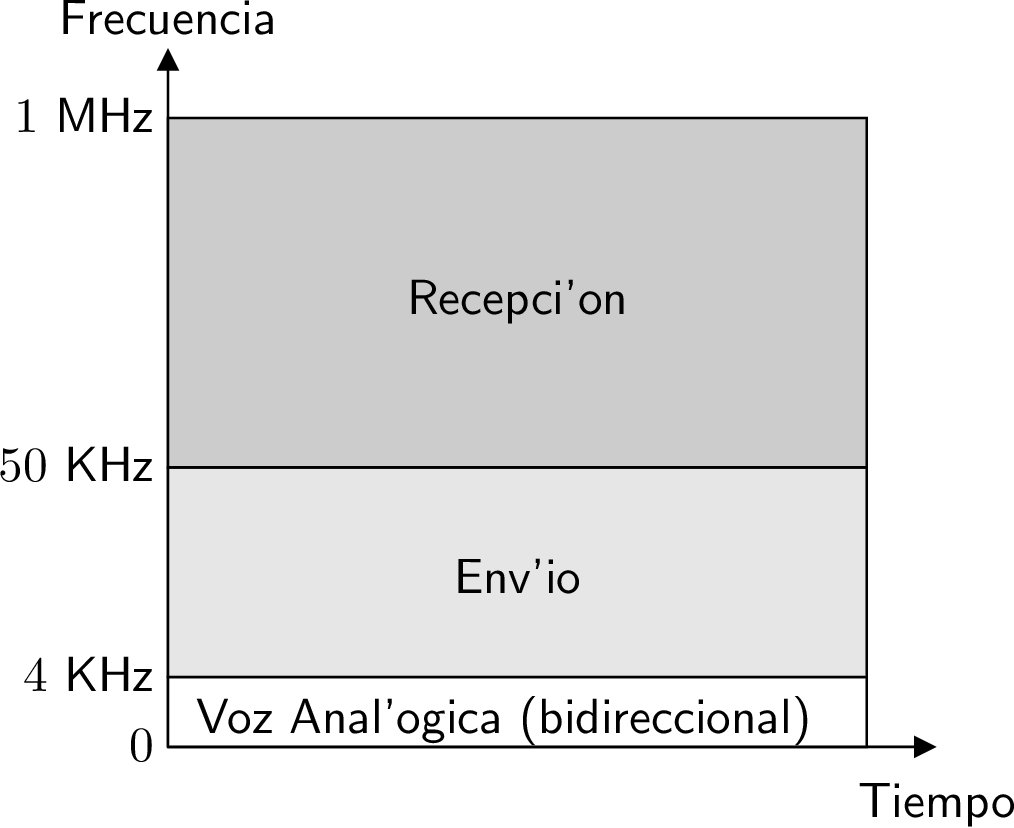
- Voice and data simultaneously (microfilters or splitter (both are a low-pass
filter with a cut-off frequency of 4 KHz) must be installed because if the
phone is not “DSL friendly”).
- Full-duplex.
3 Modulation
- FDM: voice, upstream and downstream in parallel.
- Data is modulated using:
- OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing).
- Asymmetric DSL (ADSL) uses a frequency range from approximately 20 kHz to
1 MHz.
4 Multiplexing
- Do not exist (medium is dedicated), although voice and full-duplex data
are multiplexed using FDM.
5 Delay
- Delay is minimal because the circuits are dedicated (each user has a
separate direct connection to the ISP).
- Jitter is negligible.
6 Bit-rates
- Bit-rates depends on the noise in the line. Tipically:
- Download: up to 52 Mbps.
- Upload: up to 16 Mbps.