ARP (Address Resolution Protocol)
Vicente González Ruiz
September 12, 2016
Contents
1 Funcionamiento
- RFC 826.
- Es utilizado por todos los nodos que poseen la capa de enlace de datos.
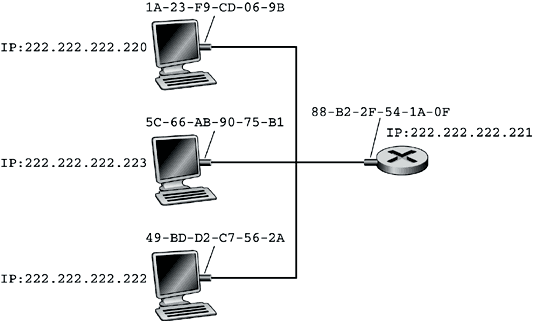
- Traduce la dirs IP a dirs f’isicas (v’ease la Figura
1).
- Cada nodo incorpora una tabla ARP que tiene la estructura:
- Las tablas ARP son generalmente din’amicas. Los nodos est’an siempre
pendientes de los frames que les llegan y utilizan las parejas de dirs IP/dirs
f’isicas (que en ellos figuran) para mantenerlas lo m’as actualizadas posible.
Adem’as, sus entradas tienen un tiempo m’aximo de vida.
- Cuando la tabla ARP no contiene una resoluci’on se ejecuta el siguiente
protocolo (ARP):
- Enviar un frame ARP a la dir de broadcast de la sub-red. Dicho frame
contiene la dir f’isica del nodo emisor y la dir IP del nodo receptor.
- Cada nodo recibe el frame ARP y comprueba si su dir IP concuerda
con la que figura en el frame. Si as’i es, contesta (usando otro frame
ARP) a la dir f’isica del nodo que quiere enviar el frame de datos.
De paso actualiza su tabla ARP.
- El nodo que quiere enviar el frame de datos recibe el segundo frame
ARP con la resoluci’on (en ’el figura la dir f’isica del nodo que lo
genera), actualiza su tabla ARP y transmite los datos.
2 Proxy ARP
- Hay routers que ejecutan (además de su tarea fundamental, el routing)
una tarea que permite mapear en sus interfaces de direcciones IP externas
a las redes que interconecta. Esto se hace mediante lo que se conoce como
proxy ARP.
- Cuando existe un router con un proxy ARP en la subred y un host
pregunta por la dirección física asignada a una dirección IP que
pertenece a una subred externa, el router responde con la dirección
física del adaptador de red por el que le llega dicha pregunta.
- Existen al menos dos casos en los que un host puede tratar de enviar
directamente un paquete a otro host, cuando éste último está en otra
subred:
- Cuando se trata de un host móvil.
- Cuando su IP no está correctamente configurado e interpreta que
el host destino está en su subred, cuando esto no es así. Esto
puede ocurrir fácilmente si se configura con una máscara de red
demasiado “grande” (demasiados ceros).
3 Inverse ARP
The Inverse Address Resolution Protocol, also called Inverse ARP, obtains Layer 3
addresses of other stations from Layer 2 addresses, such as the DLCI in Frame Relay
networks. It is primarily used in Frame Relay and ATM networks, where Layer 2
addresses of VCs are sometimes obtained from Layer 2 signaling, and the
corresponding Layer 3 addresses must be available before these VCs can be used.
Whereas ARP resolves Layer 3 addresses to Layer 2 addresses, Inverse ARP does the
opposite.